Transcription Telegram Bot
Build a Telegram bot that transcribes audio and video messages in 99 languages using TypeScript with Deno in Supabase Edge Functions.
Introduction
In this tutorial you will learn how to build a Telegram bot that transcribes audio and video messages in 99 languages using TypeScript and the ElevenLabs Scribe model via the speech to text API.
To check out what the end result will look like, you can test out the t.me/ElevenLabsScribeBot
Find the example project on GitHub.
Requirements
- An ElevenLabs account with an API key.
- A Supabase account (you can sign up for a free account via database.new).
- The Supabase CLI installed on your machine.
- The Deno runtime installed on your machine and optionally setup in your favourite IDE.
- A Telegram account.
Setup
Register a Telegram bot
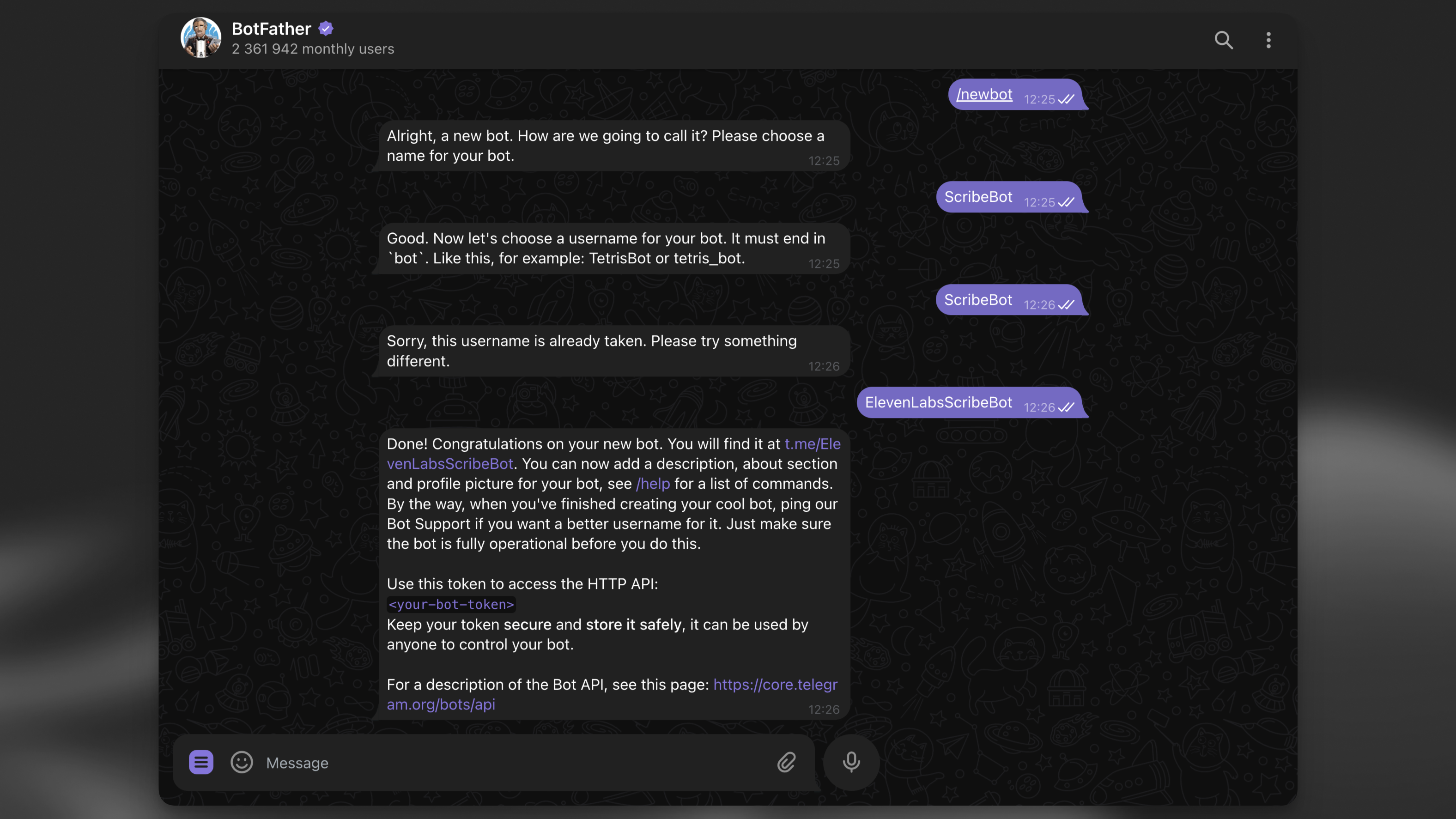
Use the BotFather to create a new Telegram bot. Run the /newbot command and follow the instructions to create a new bot. At the end, you will receive your secret bot token. Note it down securely for the next step.
Create a Supabase project locally
After installing the Supabase CLI, run the following command to create a new Supabase project locally:
1supabase initCreate a database table to log the transcription results
Next, create a new database table to log the transcription results:
1supabase migrations new initThis will create a new migration file in the supabase/migrations directory. Open the file and add the following SQL:
1234567891011121314CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS transcription_logs ( id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY, file_type VARCHAR NOT NULL, duration INTEGER NOT NULL, chat_id BIGINT NOT NULL, message_id BIGINT NOT NULL, username VARCHAR, transcript TEXT, language_code VARCHAR, created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, error TEXT);ALTER TABLE transcription_logs ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;Create a Supabase Edge Function to handle Telegram webhook requests
Next, create a new Edge Function to handle Telegram webhook requests:
1supabase functions new scribe-botIf you're using VS Code or Cursor, select y when the CLI prompts "Generate VS Code settings for Deno? [y/N]"!
Set up the environment variables
Within the supabase/functions directory, create a new .env file and add the following variables:
12345678# Find / create an API key at https://elevenlabs.io/app/settings/api-keysELEVENLABS_API_KEY=your_api_key# The bot token you received from the BotFather.TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN=your_bot_token# A random secret chosen by you to secure the function.FUNCTION_SECRET=random_secretDependencies
The project uses a couple of dependencies:
- The open-source grammY Framework to handle the Telegram webhook requests.
- The @supabase/supabase-js library to interact with the Supabase database.
- The ElevenLabs JavaScript SDK to interact with the speech-to-text API.
Since Supabase Edge Function uses the Deno runtime, you don't need to install the dependencies, rather you can import them via the npm: prefix.
Code the Telegram bot
In your newly created scribe-bot/index.ts file, add the following code:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118119120121122123124125126127128import { Bot, webhookCallback } from 'https://deno.land/x/grammy@v1.34.0/mod.ts'import 'jsr:@supabase/functions-js/edge-runtime.d.ts'import { createClient } from 'npm:@supabase/supabase-js@2'import { ElevenLabsClient } from 'npm:elevenlabs@1.50.5'console.log(`Function "elevenlabs-scribe-bot" up and running!`)const elevenLabsClient = new ElevenLabsClient({ apiKey: Deno.env.get('ELEVENLABS_API_KEY') || '',})const supabase = createClient( Deno.env.get('SUPABASE_URL') || '', Deno.env.get('SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY') || '')async function scribe({ fileURL, fileType, duration, chatId, messageId, username,}: { fileURL: string fileType: string duration: number chatId: number messageId: number username: string}) { let transcript: string | null = null let languageCode: string | null = null let errorMsg: string | null = null try { const sourceFileArrayBuffer = await fetch(fileURL).then((res) => res.arrayBuffer()) const sourceBlob = new Blob([sourceFileArrayBuffer], { type: fileType, }) const scribeResult = await elevenLabsClient.speechToText.convert({ file: sourceBlob, model_id: 'scribe_v1', tag_audio_events: false, }) transcript = scribeResult.text languageCode = scribeResult.language_code // Reply to the user with the transcript await bot.api.sendMessage(chatId, transcript, { reply_parameters: { message_id: messageId }, }) } catch (error) { errorMsg = error.message console.log(errorMsg) await bot.api.sendMessage(chatId, 'Sorry, there was an error. Please try again.', { reply_parameters: { message_id: messageId }, }) } // Write log to Supabase. const logLine = { file_type: fileType, duration, chat_id: chatId, message_id: messageId, username, language_code: languageCode, error: errorMsg, } console.log({ logLine }) await supabase.from('transcription_logs').insert({ ...logLine, transcript })}const telegramBotToken = Deno.env.get('TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN')const bot = new Bot(telegramBotToken || '')const startMessage = `Welcome to the ElevenLabs Scribe Bot\\! I can transcribe speech in 99 languages with super high accuracy\\! \nTry it out by sending or forwarding me a voice message, video, or audio file\\! \n[Learn more about Scribe](https://elevenlabs.io/speech-to-text) or [build your own bot](https://elevenlabs.io/docs/cookbooks/speech-to-text/telegram-bot)\\! `bot.command('start', (ctx) => ctx.reply(startMessage.trim(), { parse_mode: 'MarkdownV2' }))bot.on([':voice', ':audio', ':video'], async (ctx) => { try { const file = await ctx.getFile() const fileURL = `https://api.telegram.org/file/bot${telegramBotToken}/${file.file_path}` const fileMeta = ctx.message?.video ?? ctx.message?.voice ?? ctx.message?.audio if (!fileMeta) { return ctx.reply('No video|audio|voice metadata found. Please try again.') } // Run the transcription in the background. EdgeRuntime.waitUntil( scribe({ fileURL, fileType: fileMeta.mime_type!, duration: fileMeta.duration, chatId: ctx.chat.id, messageId: ctx.message?.message_id!, username: ctx.from?.username || '', }) ) // Reply to the user immediately to let them know we received their file. return ctx.reply('Received. Scribing...') } catch (error) { console.error(error) return ctx.reply( 'Sorry, there was an error getting the file. Please try again with a smaller file!' ) }})const handleUpdate = webhookCallback(bot, 'std/http')Deno.serve(async (req) => { try { const url = new URL(req.url) if (url.searchParams.get('secret') !== Deno.env.get('FUNCTION_SECRET')) { return new Response('not allowed', { status: 405 }) } return await handleUpdate(req) } catch (err) { console.error(err) }})Deploy to Supabase
If you haven't already, create a new Supabase account at database.new and link the local project to your Supabase account:
1supabase linkApply the database migrations
Run the following command to apply the database migrations from the supabase/migrations directory:
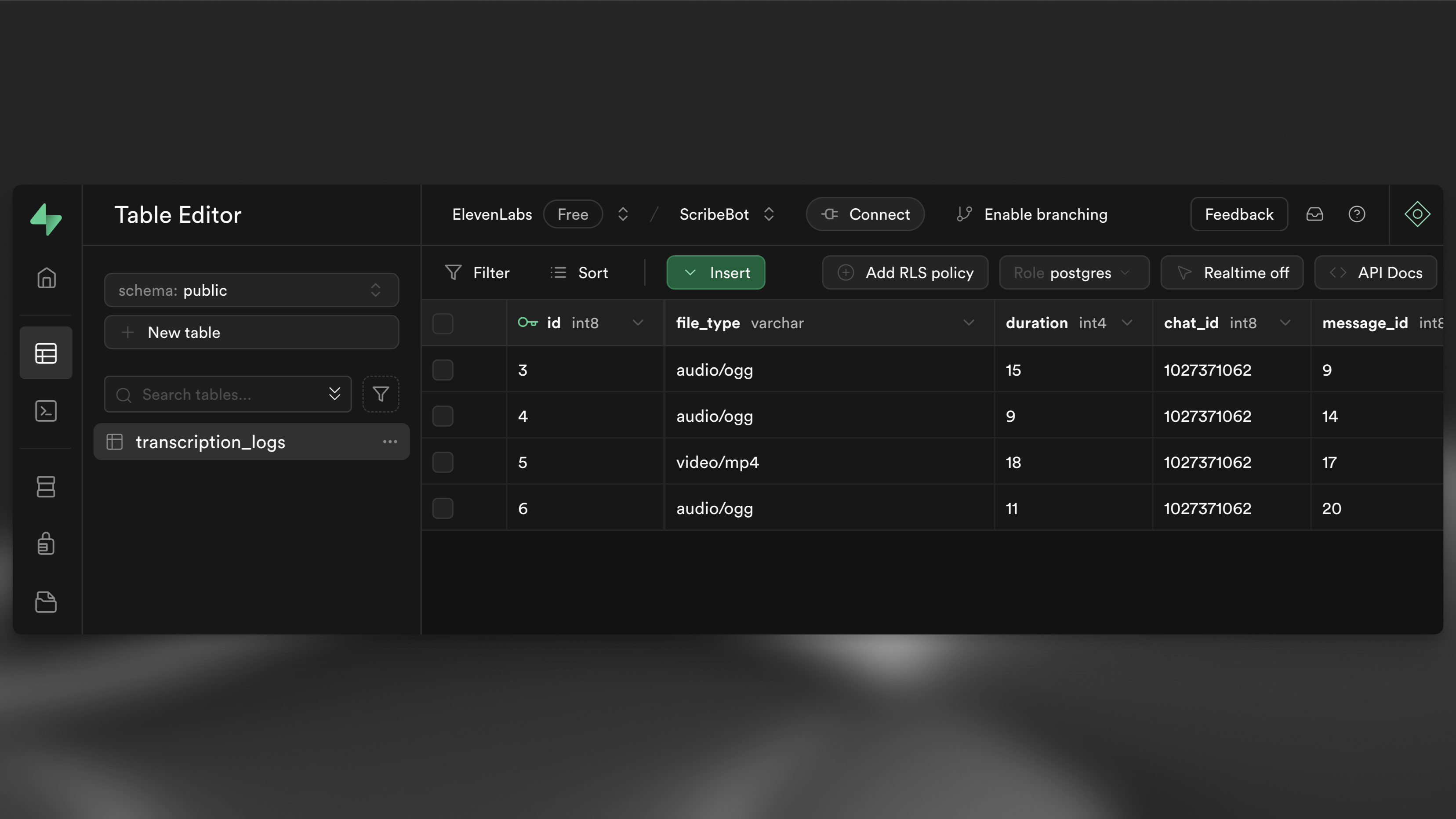
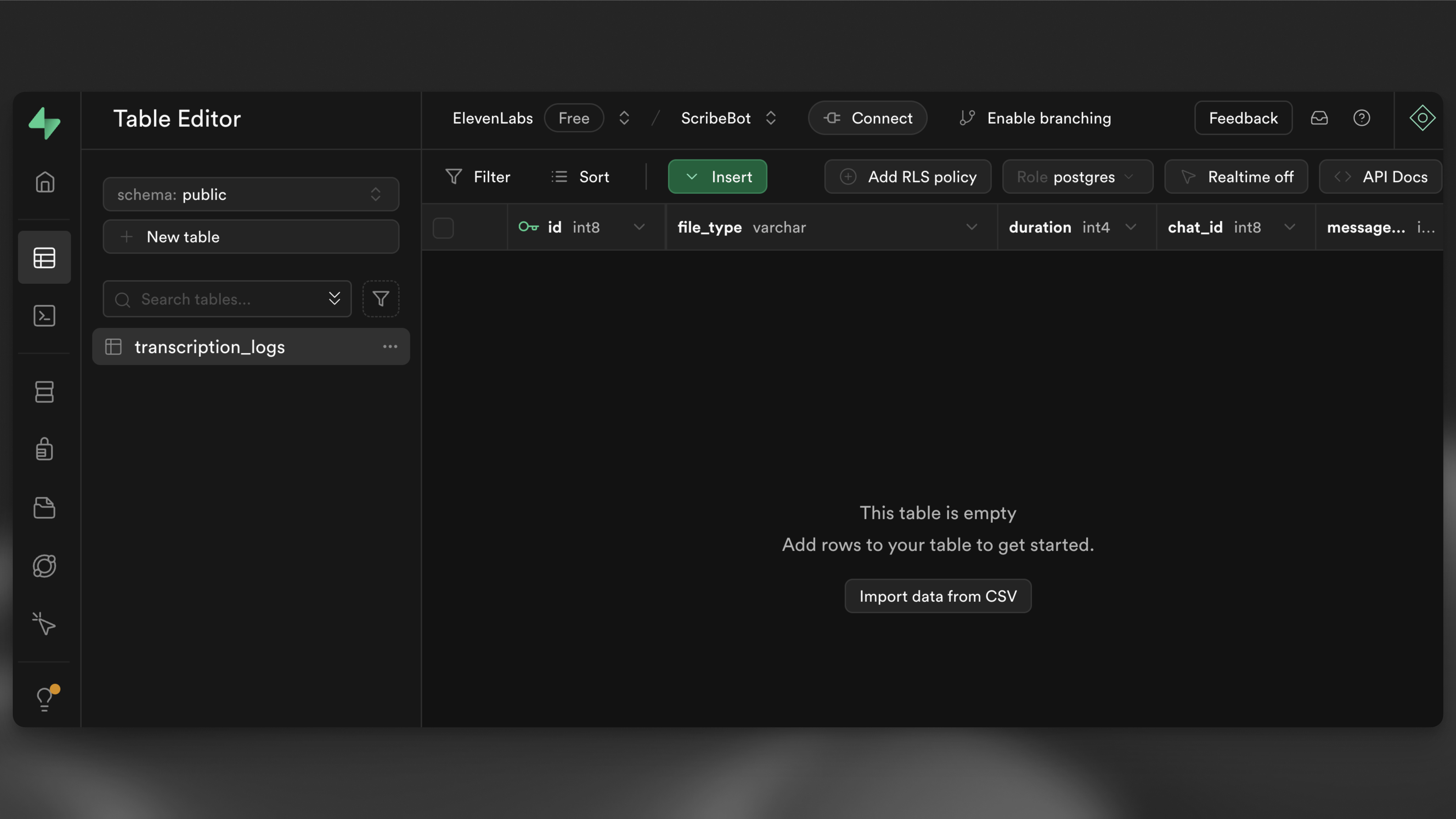
1supabase db pushNavigate to the table editor in your Supabase dashboard and you should see and empty transcription_logs table.
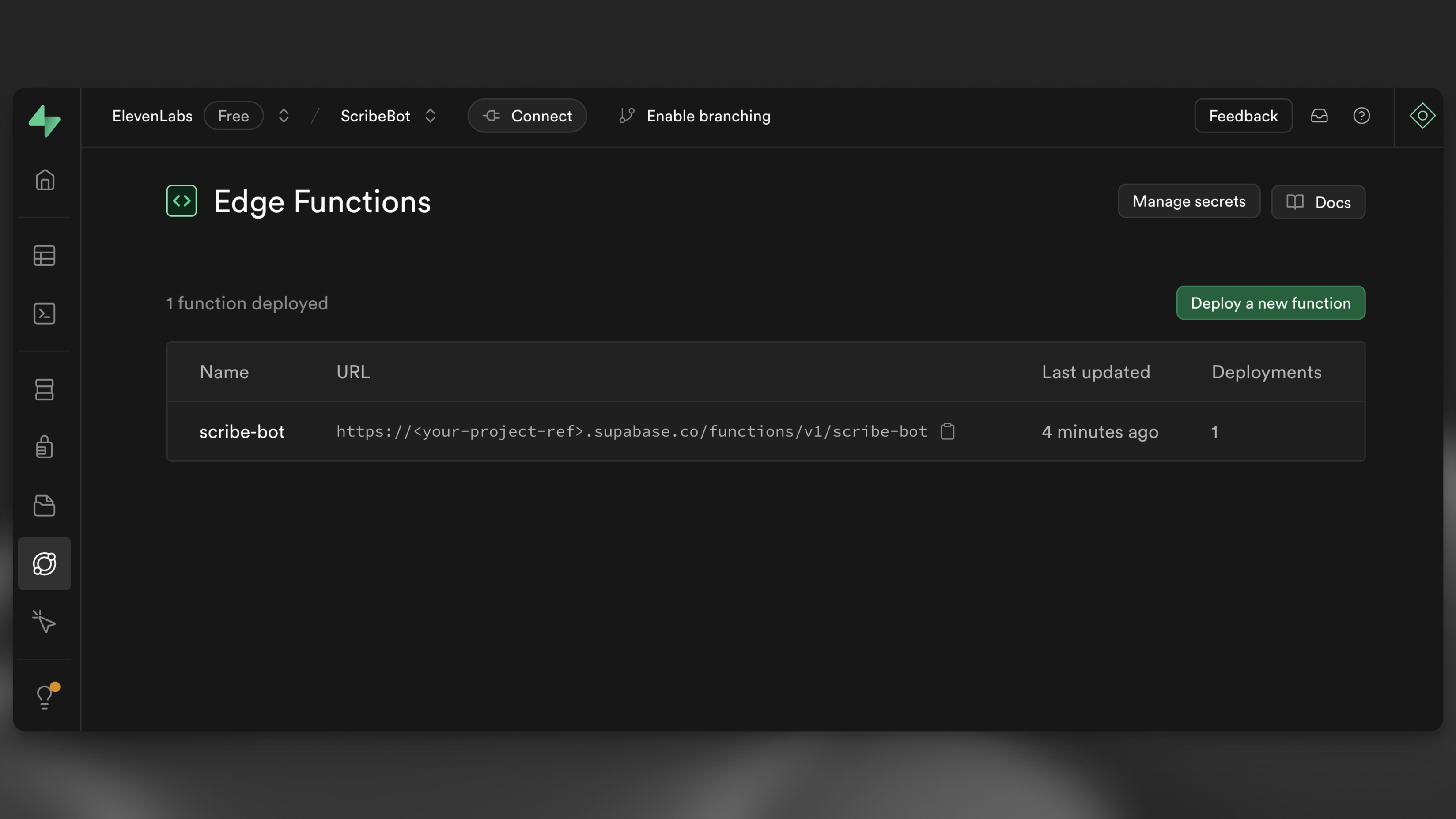
Lastly, run the following command to deploy the Edge Function:
1supabase functions deploy --no-verify-jwt scribe-botNavigate to the Edge Functions view in your Supabase dashboard and you should see the scribe-bot function deployed. Make a note of the function URL as you'll need it later, it should look something like https://<project-ref>.functions.supabase.co/scribe-bot.
Set up the webhook
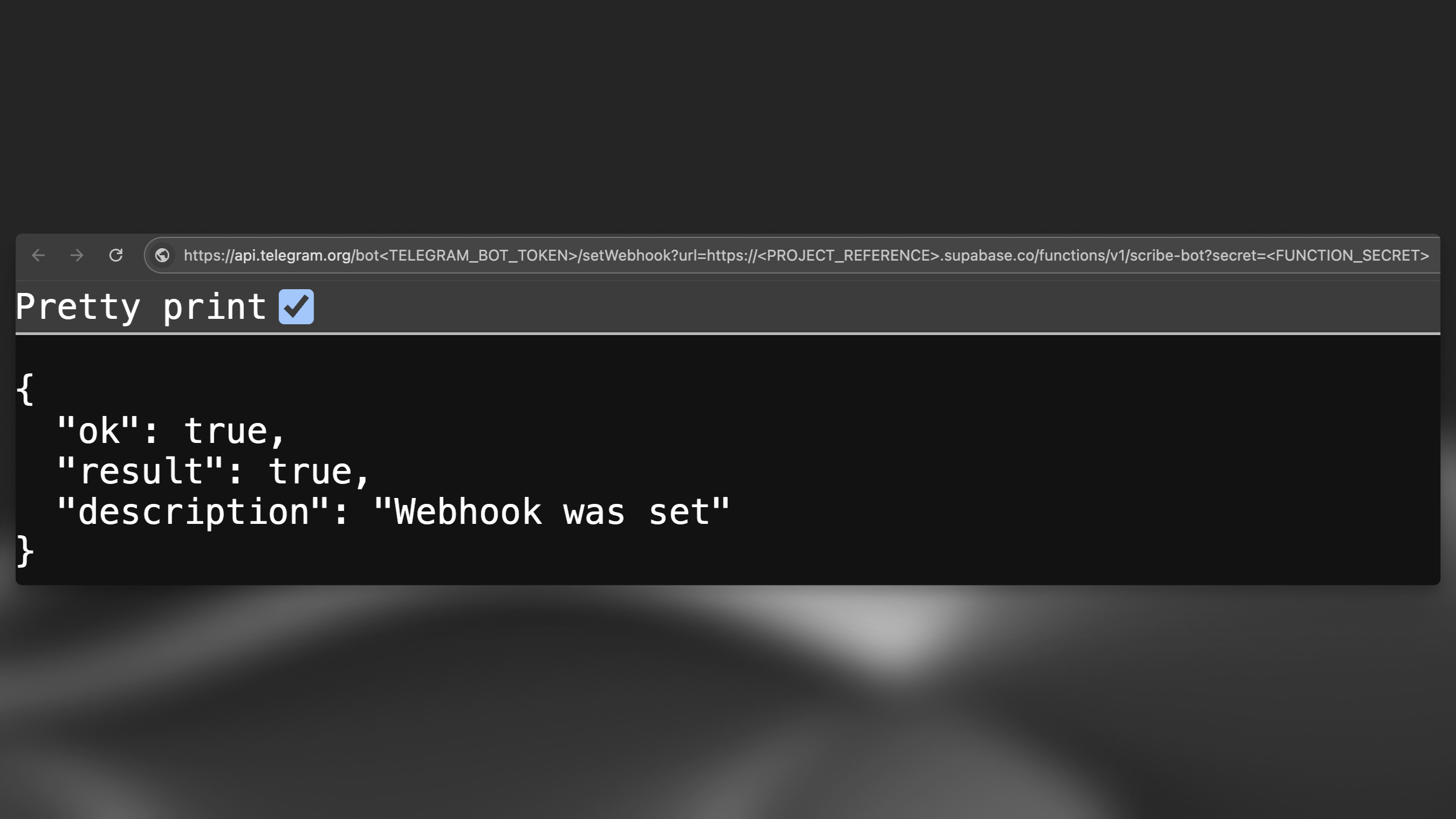
Set your bot's webhook URL to https://<PROJECT_REFERENCE>.functions.supabase.co/telegram-bot (Replacing <...> with respective values). In order to do that, run a GET request to the following URL (in your browser, for example):
1https://api.telegram.org/bot<TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN>/setWebhook?url=https://<PROJECT_REFERENCE>.supabase.co/functions/v1/scribe-bot?secret=<FUNCTION_SECRET>Note that the FUNCTION_SECRET is the secret you set in your .env file.
Set the function secrets
Now that you have all your secrets set locally, you can run the following command to set the secrets in your Supabase project:
1supabase secrets set --env-file supabase/functions/.envTest the bot
Finally you can test the bot by sending it a voice message, audio or video file.
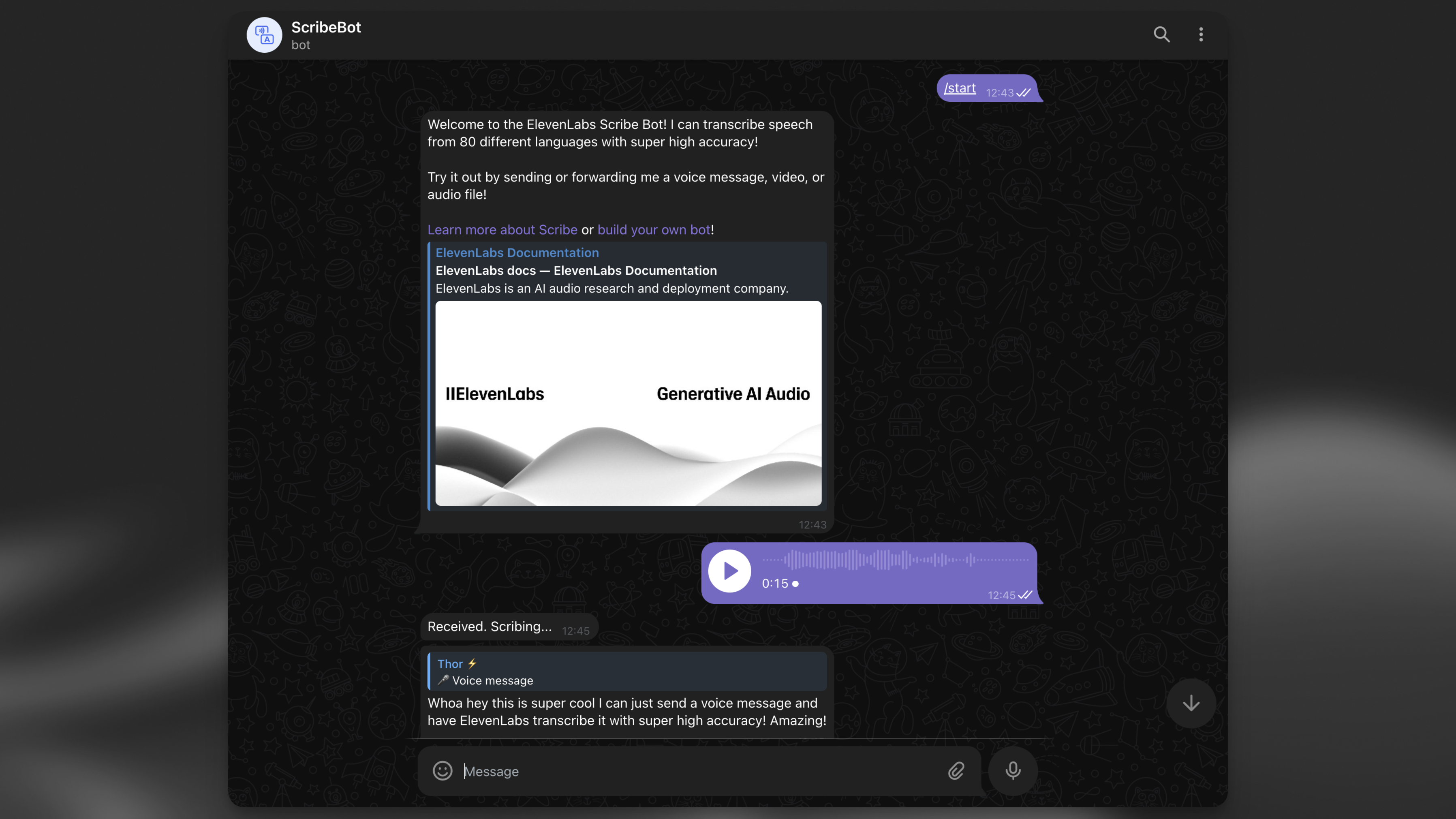
After you see the transcript as a reply, navigate back to your table editor in the Supabase dashboard and you should see a new row in your transcription_logs table.